Free Precision Engineering Image Generator
Just imagine, and we'll instantly return a variety of personalized Precision Engineering images—designed to bring your creativity to life!
- 4:3
- 3:4
- 1:1

image.state.default








Related Tags
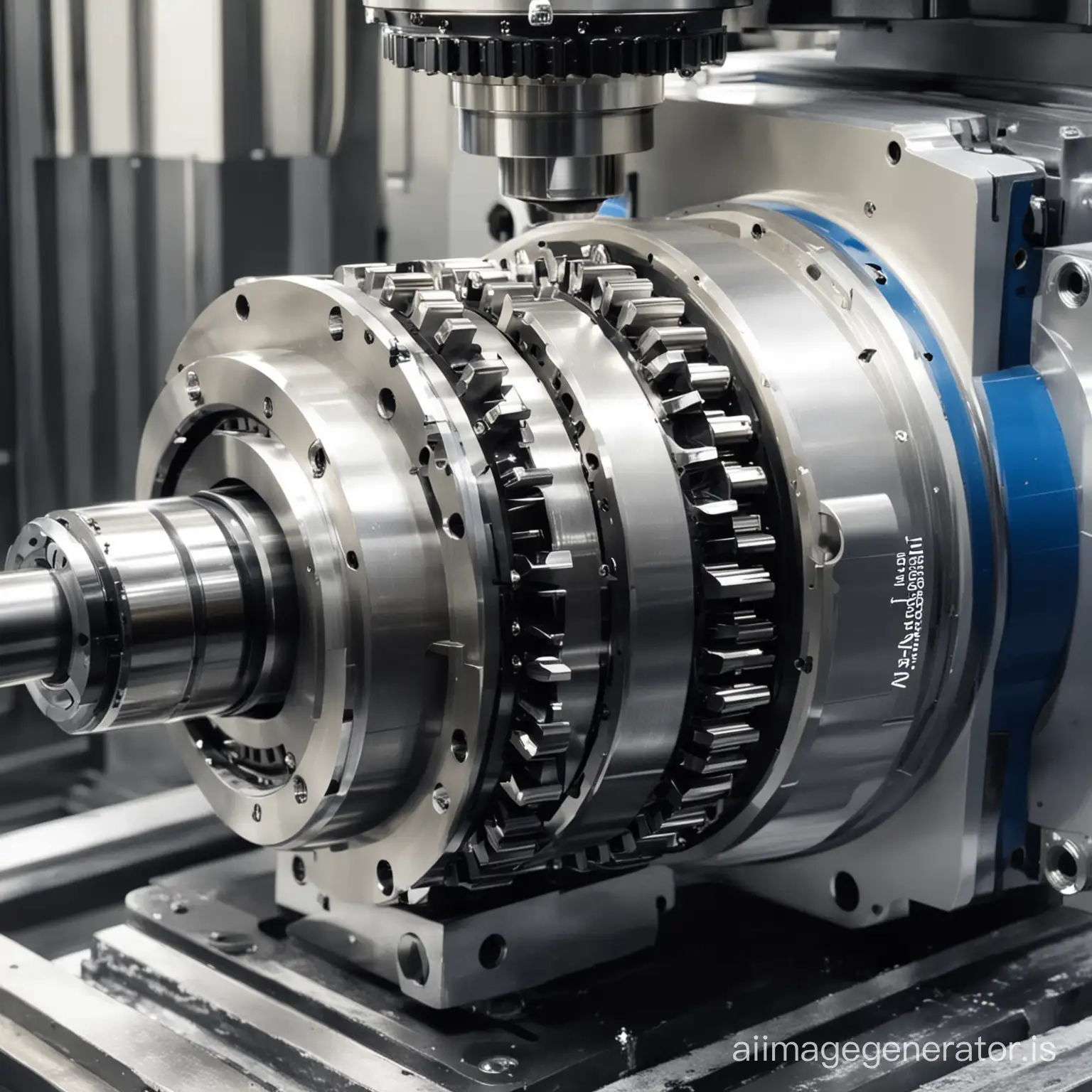
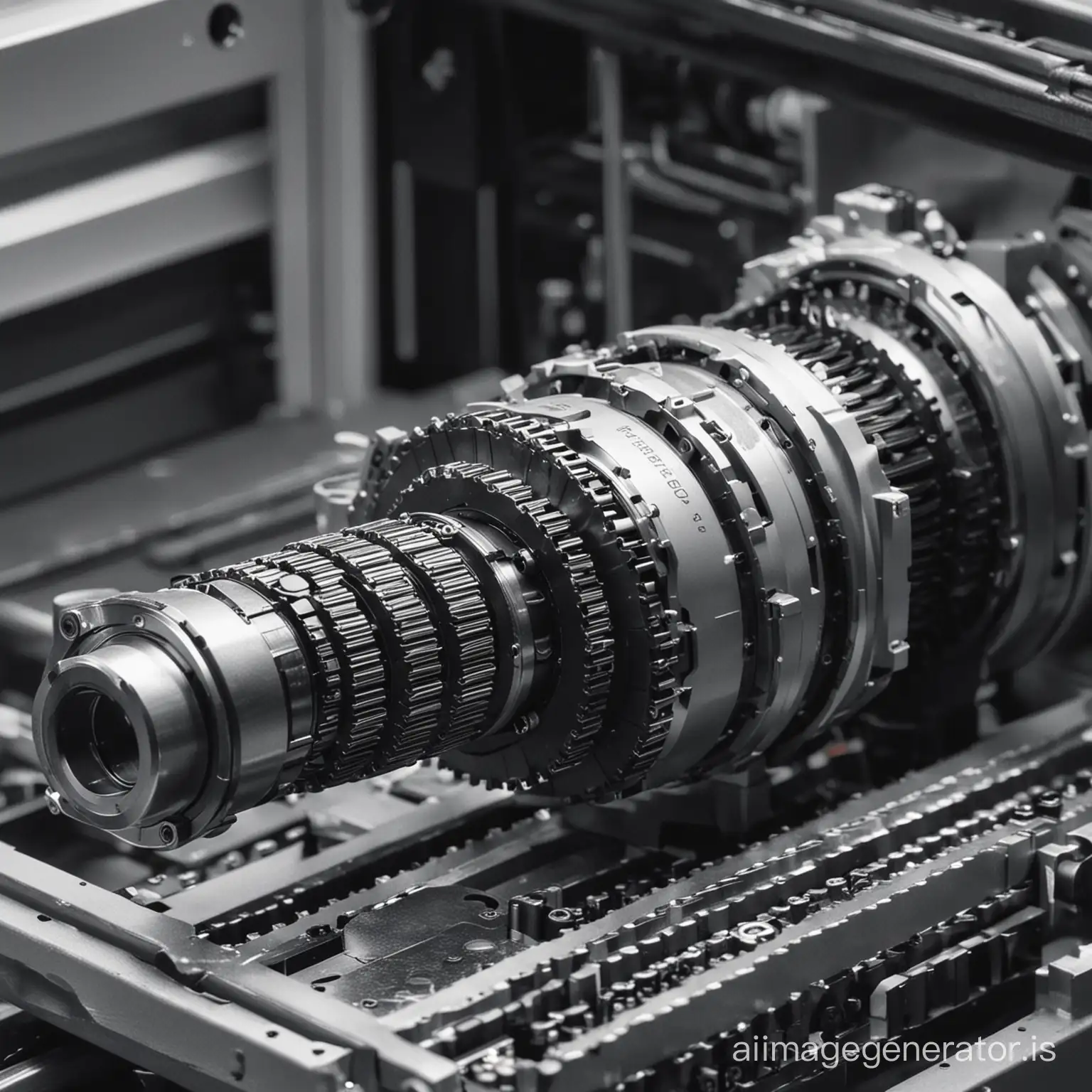
Precision engineering is a sub-discipline of engineering that focuses on designing machines, fixtures, and other structures that have exceptionally low tolerances and are stable over time. This field involves the creation of extremely accurate and precise components, often for use in technology sectors like aerospace, medical devices, and robotics. The principles of precision engineering are essential for developing high-quality products that require minimal error margins.
Understanding Precision Engineering: A Comprehensive Overview
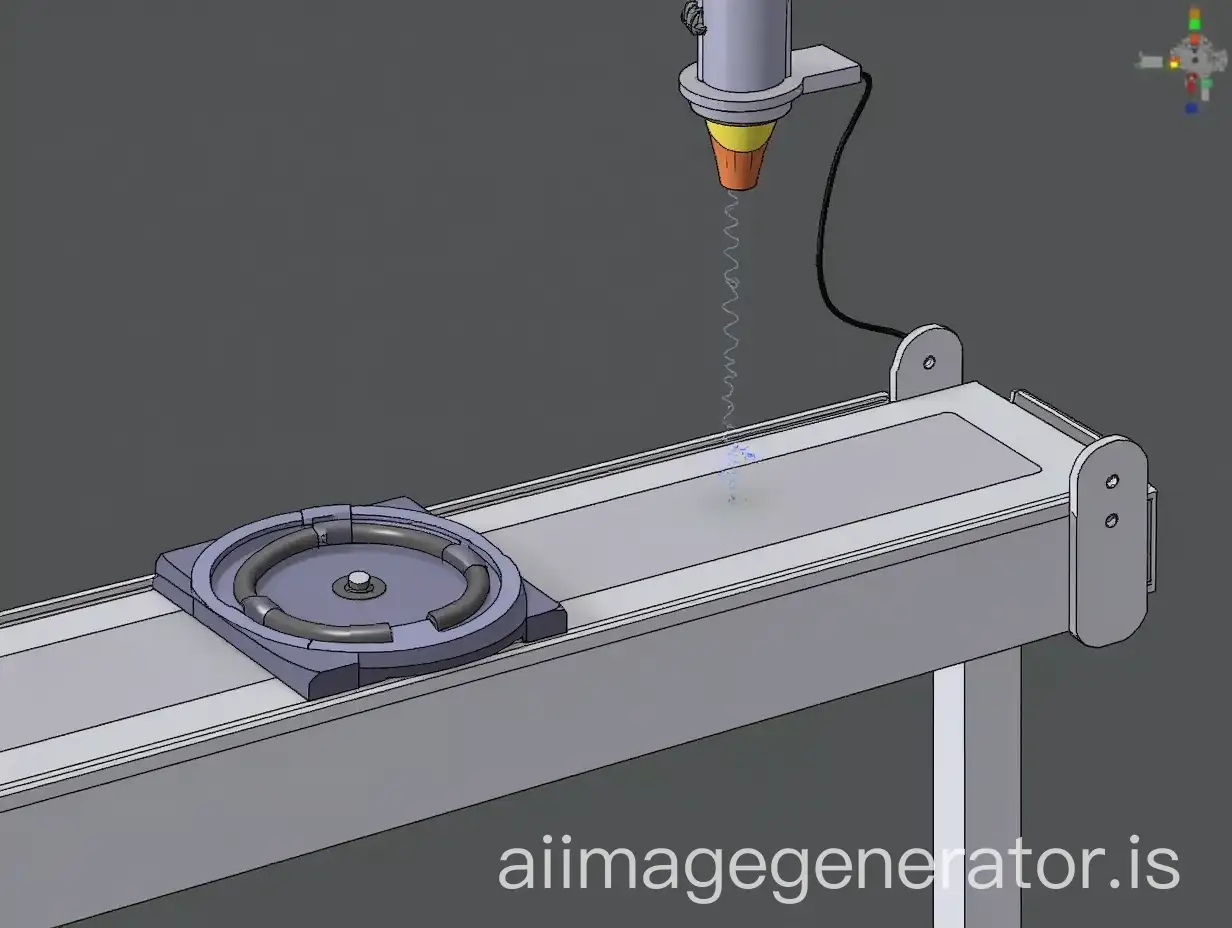
Precision engineering is characterized by its emphasis on accuracy, repeatability, and reliability. Applications range from the manufacturing of small-scale components like microchips and medical instruments to large-scale systems such as aerospace assemblies and automotive parts. The precision in these components is critical to ensuring the functionality and safety of complex systems. Advanced techniques such as CNC machining, laser cutting, and 3D printing are commonly used in precision engineering.
Key Characteristics and Applications of Precision Engineering
Throughout history, numerous innovations and pioneers have shaped the field of precision engineering. Notable figures include Carl Zeiss, whose advancements in optical instruments revolutionized the field of microscopy, and Henry Maudslay, who developed the screw-cutting lathe, a fundamental tool in modern engineering. Innovations such as Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) and precision lathes have greatly enhanced the capabilities of precision manufacturing, allowing for the production of complex and highly accurate components.
Influential Innovations and Pioneers in Precision Engineering
The future of precision engineering is poised for exciting developments driven by advancements in technology. Emerging trends include the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to optimize manufacturing processes and improve precision. The use of nanotechnology and advanced materials is also expanding the boundaries of what is possible in precision engineering, enabling the creation of components at an atomic scale. Additionally, the increasing demand for miniaturization in electronics and medical devices continues to push the limits of precision engineering.
Future Development Trends in Precision Engineering